Step by Step Guide to Process Mining
Process mining is a powerful tool that helps businesses understand and improve their operations. It analyzes data from everyday activities, like processing orders or handling customer inquiries, to show how work is really getting done.
Modern businesses rely on efficiency to save time and money. Process mining not only highlights hidden problems but also shows where resources are being wasted or delays are happening. By using these insights, companies can cut costs, speed up processes, and make smarter decisions.
This guide will take you through the steps to get started with process mining. Whether you’re looking to optimize workflows, boost productivity, or gain a competitive edge, this guide is designed to help you unlock the full potential of process mining. Let’s dive in!

Step-by-Step Process Mining Guide
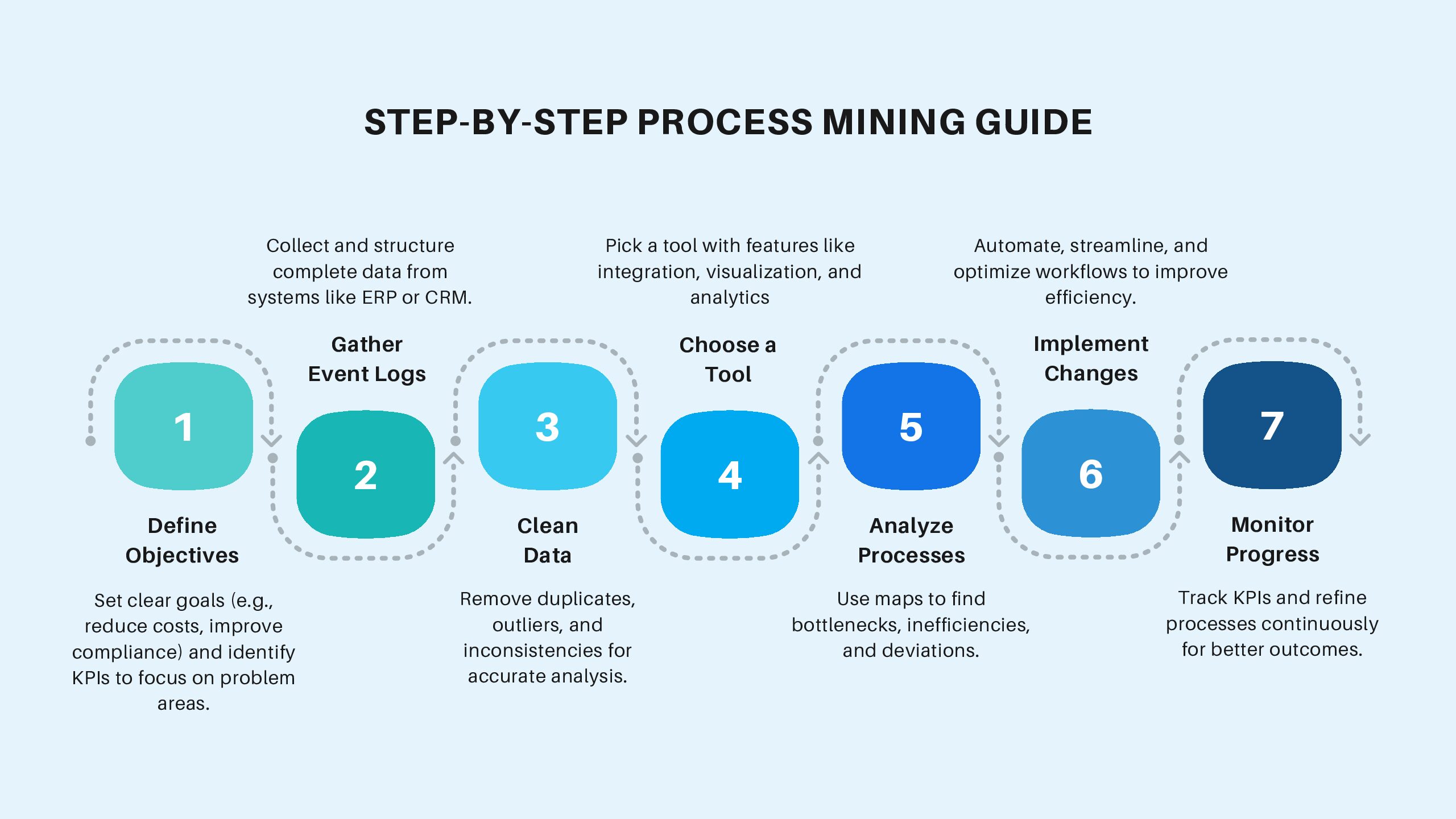
Step 1: Define Objectives
The first step in process mining is to establish clear objectives. Knowing what you want to achieve will guide your efforts and ensure you focus on the right processes.
- Identify Business Goals:
Think about the outcomes you want. Are you aiming to reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, or streamline operations? Start by pinpointing the key performance indicators (KPIs) you want to improve. - Pinpoint Problem Areas:
Examine your existing workflows and identify recurring issues. Are there delays, bottlenecks, or inconsistencies? For example:- Bottlenecks: Is one step in your workflow slowing everything down?
- Compliance Issues: Are processes consistently following legal or company standards?
- Cost Inefficiencies: Are there areas where resources are being wasted?
- Set Specific Objectives:
Once you know your goals, define them in measurable terms. Some examples include:- Reducing processing time for customer orders by 20%.
- Achieving 100% compliance with regulatory standards.
- Cutting operational costs in a specific department by 10%.
By setting clear and actionable objectives, you create a strong foundation for the process mining project.
Step 2: Gather Event Logs
Event logs are the raw data that power process mining. These logs capture information about activities, such as who performed them, when they occurred, and their outcomes.
- Find Data Sources:
Event logs can come from many systems within your business, such as:- ERP Systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle): For data on procurement, production, and inventory management.
- CRM Systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot): For insights into customer interactions and sales pipelines.
- IT Systems: For tracking support tickets, system usage, or IT service management processes.
- Ensure Data Completeness:
The quality of your event logs will directly impact the effectiveness of your analysis. To ensure you have usable data:- Check for Missing Entries: Ensure every step of the process is logged.
- Verify Accuracy: Make sure timestamps, identifiers, and activity descriptions are correct.
- Consolidate Data Sources: Combine data from multiple systems to get a comprehensive view of the process.
- Organize the Data:
Structure your event logs with these key components:- Case ID: A unique identifier for each process instance (e.g., an order number).
- Activity Name: The specific action taken (e.g., “Order Received”).
- Timestamp: The date and time the activity occurred.
Step 3: Clean and Prepare Data
Data cleaning is a crucial step in process mining because the quality of your analysis depends on the accuracy of your data. Poor-quality data can lead to incorrect conclusions and wasted efforts.
1. Importance of Data Cleaning
- Ensures your event logs accurately represent the actual processes.
- Eliminates noise and irrelevant information that can distort results.
- Makes it easier to identify patterns, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies.
2. Common Challenges and How to Address Them
- Missing Data:
- Challenge: Some events may not have been recorded due to system errors or incomplete processes.
- Solution: Cross-check logs with other data sources to fill in the gaps where possible. Use data interpolation techniques to estimate missing values if necessary.
- Duplicates:
- Challenge: Duplicate entries can inflate activity counts or misrepresent process flows.
- Solution: Use automated tools or scripts to identify and remove duplicate records. Ensure unique identifiers like Case IDs are consistent.
- Inconsistent Data Formats:
- Challenge: Different systems may log data in various formats (e.g., date formats, activity names).
- Solution: Standardize all data into a single format before analysis.
- Outliers and Irrelevant Data:
- Challenge: Unusual data points or irrelevant records can skew the analysis.
- Solution: Remove outliers that don’t fit the context of your analysis and filter data to include only relevant cases and activities.
Taking the time to clean and prepare your data will ensure your process mining results are both accurate and actionable.
Step 4: Choose the Right Process Mining Tool
Selecting the right tool is essential for successful process mining. The tool you choose should align with your business needs and technical capabilities.
1. Overview of Popular Tools
- Mindzie, process mining software:
- Known for its user-friendly interface and robust analytics capabilities.
- Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses looking for quick insights.
- Disco:
- Focused on intuitive process visualization and analysis.
- Great for those new to process mining.
- UiPath Process Mining:
- Integrates with automation tools, making it perfect for businesses implementing RPA (Robotic Process Automation).
2. Key Features to Look For
- Ease of Use:
- Intuitive dashboards and simple navigation for non-technical users.
- Integration:
- Ability to connect with your existing systems like ERP, CRM, and IT systems.
- Data Handling:
- Robust tools for data cleaning, preparation, and transformation.
- Process Visualization:
- Clear and customizable process maps and flowcharts.
- Analytics and Insights:
- Built-in KPIs, root cause analysis, and anomaly detection.
- Scalability:
- Supports growth as your business needs evolve.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Pricing that aligns with your budget and offers a good return on investment.
Step 5: Analyze and Visualize the Processes
This step involves turning raw data into clear, visual representations of your processes. The goal is to understand how things are working and pinpoint areas for improvement.
1. Creating Process Maps and Flowcharts
- Process Maps: These diagrams show the exact flow of activities, making it easy to see how tasks move from one step to the next.
- Flowcharts: These help break down complex workflows into simple, visual sequences.
- Use your process mining tool to generate these visualizations based on the cleaned data.
2. Identifying Bottlenecks, Deviations, and Inefficiencies
- Bottlenecks: Look for points in the process where tasks slow down or pile up, causing delays.
- Example: A high volume of orders waiting for approval in a single step.
- Deviations: Spot activities that don’t align with the intended process flow.
- Example: An approval step being skipped or handled out of order.
- Inefficiencies: Identify areas where time, effort, or resources are being wasted.
- Example: Duplicate tasks or unnecessary approvals.
By analyzing and visualizing your processes, you gain actionable insights into where and how improvements can be made.
Step 6: Implement Insights
Once you’ve identified issues, it’s time to act on the findings to make tangible improvements.
1. Examples of Actionable Changes
- Streamline Workflow: Eliminate redundant tasks or combine steps to speed up processes.
- Example: Automate repetitive data entry tasks using RPA.
- Redistribute Resources: Allocate more resources to bottlenecked steps to reduce delays.
- Example: Assign additional team members to handle order approvals during peak times.
- Enhance Compliance: Enforce rules and guidelines for process consistency.
- Example: Set up automatic checks to ensure no step is skipped.
2. Strategies for Process Improvement
- Lean Principles: Remove waste and focus only on activities that add value.
- Automation: Use technology to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up employees for more critical work.
- Employee Training: Ensure staff understands and follows optimized workflows.
- Feedback Loops: Gather input from employees and stakeholders to refine changes.
By implementing these insights, you can create more efficient, cost-effective processes that align with your objectives.
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize
Process mining is not a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing journey of improvement. Continuous monitoring helps ensure changes are effective and processes stay efficient.
1. Setting Up Continuous Monitoring
- Real-Time Dashboards: Use your process mining tool to track workflows in real-time.
- Automated Alerts: Set up notifications for deviations or potential issues.
- Example: Get an alert when a step takes longer than the expected time.
2. The Role of KPIs in Measuring Success
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track improvements.
- Examples:
- Average processing time.
- Number of completed tasks per day.
- Compliance rates with the defined process.
- Examples:
- Compare these KPIs before and after implementing changes to measure progress.
3. Importance of Iteration in Process Mining
- Analyze Results: Use KPI data to assess the success of your changes.
- Refine Processes: Address new issues or inefficiencies as they arise.
- Stay Agile: Continuously adapt to changes in business needs, technology, or regulations.
Common Challenges in Process Mining
While process mining can provide significant benefits, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these obstacles can help organizations address them effectively and ensure a smooth process mining journey.
1. Data Integration Issues
- Challenge:
Data required for process mining often resides in multiple systems, such as ERP, CRM, or custom IT applications. Integrating this data can be complex due to differing formats, structures, or system limitations. - Solution:
- Use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools to consolidate data into a unified format.
- Collaborate with IT teams to ensure smooth data extraction and integration.
- Invest in process mining tools with built-in data integration capabilities.
2. Resistance to Change Within Organizations
- Challenge:
Employees may fear that process mining will expose inefficiencies or lead to job automation, resulting in resistance to adopting the technology. - Solution:
- Involve employees early in the process mining journey.
- Communicate how process mining benefits both the organization and employees, such as reducing repetitive tasks.
- Provide training to help employees adapt to new workflows and tools.
3. Overcoming Skill Gaps in Process Mining Expertise
- Challenge:
Process mining requires technical skills and domain expertise that may be lacking in an organization. - Solution:
- Upskill teams through training and certifications in process mining.
- Hire consultants or experts for the initial setup and knowledge transfer.
- Choose tools with intuitive interfaces that require minimal technical expertise.
Tips for Addressing These Challenges of Process Mining
- Start small: Pilot process mining in a specific department before scaling up.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement to encourage buy-in from all levels of the organization.
- Partner with vendors who provide strong customer support and training.
Conclusion
Process mining is a powerful tool for modern businesses to uncover inefficiencies, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions. By analyzing workflows and gaining actionable insights, organizations can achieve cost savings, enhanced productivity, and better compliance.
Starting small—perhaps with a pilot project in a single department—can help you build confidence in the process. From there, you can scale up to tackle larger challenges and unlock the full potential of process optimization.
Now is the perfect time to explore process mining tools, gather your data, and take the first step on this transformative journey. With the right approach, process mining can be the key to sustained growth and innovation in your organization.
FAQs About Process Mining
1. What Industries Benefit Most from Process Mining?
Process mining is valuable across a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: For optimizing production workflows and reducing waste.
- Healthcare: To ensure compliance and improve patient care processes.
- Finance: For streamlining invoicing, auditing, and regulatory reporting.
- Retail and E-commerce: To enhance order fulfillment and supply chain efficiency.
- Logistics: For reducing delivery times and improving route optimization.
2. How Long Does It Take to Implement Process Mining?
The timeline for implementing process mining varies depending on factors like data complexity, tool selection, and organizational readiness. Typically:
- Small Projects: 1–3 months for setup and initial insights.
- Larger Initiatives: 6–12 months for enterprise-wide adoption and optimization.
3. Is Process Mining Only for Large Enterprises?
No, process mining is not limited to large enterprises. While it’s often associated with big companies, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can also benefit. Many tools cater to different organizational sizes and budgets, making it accessible for businesses of all scales.
By addressing these common questions, businesses can better understand the value and feasibility of integrating process mining into their operations.
Daniel is a 20 year ventran in enterprise software sales with over 7 years experience helping businesses drive operational excellence.