Process Mining Example: A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementation in Your Organization
Process mining is a technique that analyzes business operations by extracting data from event logs. It visualizes real-time workflows, identifies inefficiencies, and helps businesses optimize processes. Think of it as a tool that offers a clear view of how work actually gets done within an organization. In today’s competitive market, organizations need efficient, data-driven methods to improve operations. Process mining offers actionable insights that traditional methods often miss, helping businesses simplify workflows, reduce costs, and improve decision-making.
This article explores process mining, its real-world applications, and how to implement it in your organization. We’ll cover its benefits, challenges, and practical steps for adoption, offering valuable insights for business leaders and tech professionals. Based on expert knowledge and successful case studies, this article provides reliable, actionable information. It’s backed by industry reports and expert reviews, ensuring you get credible insights to understand and implement process mining effectively.
What is Process Mining?
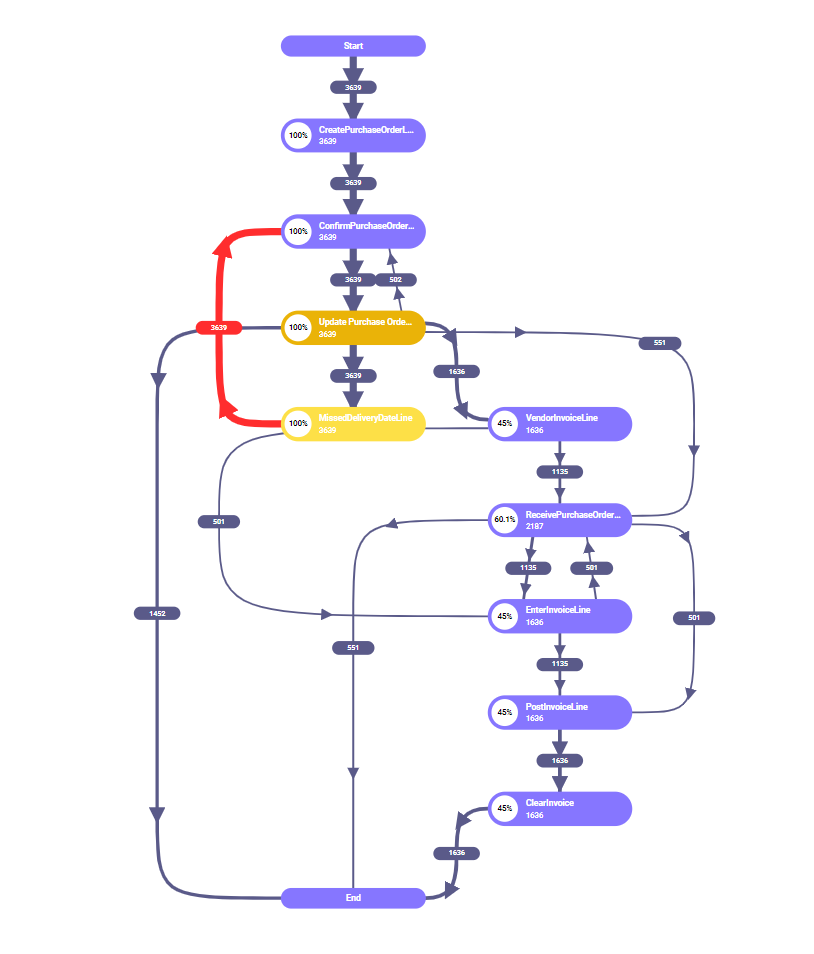
Process mining is a technique that uses data from business systems to map and analyze how processes are actually carried out. It focuses on three main pillars:
- Data Mining: Extracting relevant data from event logs.
- Process Modeling: Creating a visual representation of the actual workflows.
- Analysis: Analyzing the processes to uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement.
How Process Mining Works
The process mining approach involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from event logs generated by systems (e.g., ERP, CRM).
- Event Logs: These logs record the actions, timestamps, and other details of each process step.
- Analysis: Using algorithms to compare the recorded data with predefined process models, identifying discrepancies and optimization opportunities.
Relation to Other Analytical Methods
Unlike traditional business intelligence, which relies on aggregated data reports, process mining provides a detailed view of the actual processes in action. While business intelligence offers insights based on past data, process mining allows for real-time process optimization and data-driven decision-making, offering a deeper understanding of how work truly flows.
Key Benefits of Process Mining
Improved Process Visibility
Process mining provides a clear, data-driven view of your business operations. It uncovers the actual flow of processes, revealing hidden inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and deviations from the ideal process. This visibility enables businesses to make informed decisions on where to focus improvement efforts.
Increased Efficiency and Performance
By identifying inefficiencies, process mining helps businesses save time and money. For example, a manufacturing company could reduce production delays by pinpointing where machine downtime occurs, or an e-commerce company might simplify order fulfillment by uncovering redundant steps in their processes.
Better Decision-Making
With real-time data and insights into operational performance, businesses can make smarter, evidence-based decisions. Process mining helps leaders identify areas for improvement, forecast future trends, and optimize resources, leading to better strategic planning.
Compliance and Risk Management
Process mining helps organizations ensure compliance with industry regulations by providing a transparent view of processes and highlighting areas where rules may not be followed. It also helps mitigate risks by detecting potential issues early, reducing the chance of non-compliance or fraud.
Real-Life Process Mining Examples
Example 1: Manufacturing Industry
In a large automotive manufacturing plant, process mining was applied to optimize the production workflow. The company collected event log data from machinery, operators, and maintenance systems to map out the entire production process. Through this data analysis, process mining uncovered significant delays at specific stages, particularly during the assembly line when certain machines were undergoing unscheduled downtime, which affected the overall throughput.
With this visibility, the plant management team could predict when machines were likely to break down based on historical patterns, allowing for predictive maintenance scheduling. Additionally, process mining highlighted inefficiencies in the allocation of resources—such as workers being assigned to stations with minimal work during downtime periods. By adjusting staffing levels based on real-time demand, the company improved resource utilization. As a result, the plant reduced idle time by 20%, improved production speed, and saved on maintenance costs.
Source: Process Mining in the Manufacturing Industry – Deloitte Insights, 2020
Example 2: Healthcare Sector
In a busy metropolitan hospital, process mining was used to address patient flow issues that were leading to excessive waiting times in the emergency department (ED). The hospital used event log data from patient check-ins, triage, treatment, and discharge stages to map the entire patient journey through the ED.
Process mining revealed that significant delays occurred during the handoff process between departments, particularly when patients moved from triage to diagnostic imaging or treatment. Additionally, there were inefficiencies in staff scheduling, with certain shifts having too many or too few healthcare providers available. With these insights, the hospital restructured its workflow, optimized staffing based on peak patient arrival times, and created more efficient patient routing. As a result, patient waiting times were reduced by 30%, and the hospital was able to increase its patient capacity by 15% without adding additional staff, leading to better care delivery and improved patient satisfaction.
Source: Process Mining in Healthcare – HealthITAnalytics, 2021
Example 3: Financial Services
In the financial services industry, a major insurance company implemented process mining to detect fraud patterns and optimize claims processing. By analyzing event log data from its claims management system, process mining uncovered irregularities in claims patterns that were difficult to detect manually. For instance, the company found that certain claims were being processed rapidly without the usual checks, and others showed unusual repetition of claim types across multiple claims.
The analysis led to the discovery of a group of fraudulent claims where the same individuals had submitted multiple claims for the same incidents under different aliases. Process mining also revealed inefficiencies in the claims approval process, where claims were taking longer than necessary due to redundant verification steps. The company implemented automated fraud detection rules and simplified the claims process by eliminating unnecessary steps. This resulted in a 25% reduction in fraud-related payouts, quicker claims processing, and a 40% increase in customer satisfaction due to faster claim resolutions.
Source: Process Mining for Fraud Detection in Insurance – Accenture, 2020
Example 4: Retail and E-commerce
A major e-commerce retailer used process mining to improve its supply chain and optimize the customer journey. The company tracked customer interactions from the moment they visited the website through checkout, payment, and order fulfillment. By analyzing event logs from website clicks, cart abandonment, order processing, and inventory management, process mining revealed several key areas of improvement.
The first insight came from the identification of mismatched stock levels that led to delays in fulfilling orders. Process mining pinpointed specific products that were frequently out of stock, causing fulfillment delays and negatively affecting the customer experience. Additionally, it highlighted inefficiencies in the order routing process, where orders from certain regions were sent through longer delivery routes, resulting in unnecessary shipping delays.
Using the insights from process mining, the company optimized its inventory management system to better forecast demand, implemented more efficient warehouse routing, and simplified its delivery network. The result was a 15% reduction in order fulfillment time, a 10% decrease in cart abandonment rates, and a significant improvement in customer satisfaction, leading to increased sales and repeat customers.
Source: How Process Mining Helps Retailers – McKinsey & Company, 2021
How to Implement Process Mining in Your Organization?
Step-by-Step Guide
- Define Objectives
Set clear goals for process mining (e.g., improving efficiency, reducing costs, ensuring compliance). - Data Collection
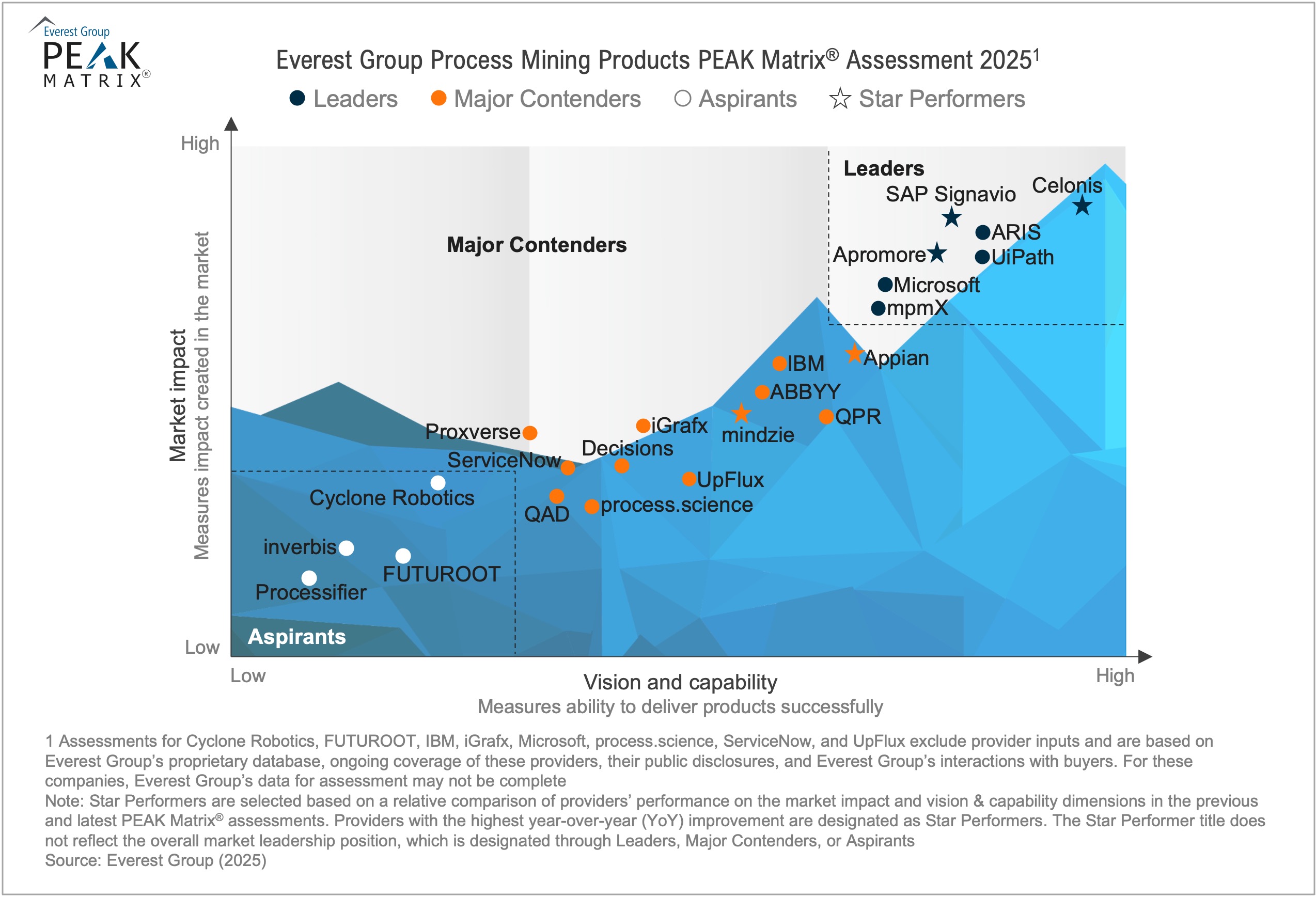
Gather event log data from systems like ERP, CRM, and workflow tools. - Select the Right Tool
Choose a process mining tool that aligns with your needs (e.g., Celonis, Disco, PAFnow). - Model and Analyze
Use the tool to visualize processes and identify inefficiencies. - Implement Changes
Make improvements based on the insights gained. - Monitor and Optimize
Continuously track performance and refine processes.
Conclusion
Implementing process mining can significantly improve your organization’s operational efficiency, decision-making, and overall performance. By following a clear, step-by-step approach—from defining your objectives and collecting the right data to choosing the best tools and continuously optimizing processes—you can unlock valuable insights that drive meaningful improvements.
While challenges such as data quality and system integration can arise, selecting the right process mining tool—like Mindzie—can help address these issues. Mindzie offers powerful, scalable solutions that integrate smoothly with existing systems, providing intuitive insights to optimize your processes and maximize efficiency. With the right tools, you’ll be well on your way to transforming your business operations and staying ahead in today’s competitive market.
Daniel is a 20 year ventran in enterprise software sales with over 7 years experience helping businesses drive operational excellence.